SentryBox has been discontinued. Thank you for being part of the journey — learn more in our blog post

Hackers might already be inside your network, often remaining undetected for an average
of 98 days. During this time, they move laterally from device to device,
slowly taking over the entire network.
The End Goal: Steal Data or Launch Ransomware
Attacks
By deploying honeypots of various kinds within the network, you gain visibility. These
honeypots resemble potential targets, enticing cyber attackers to engage with them. Since the attackers are
often operating remotely, with limited means to physically verify what they are attacking, they are compelled
to act quickly before detection.
They will attempt to fingerprint devices, exploit services like HTTP, SSH, FTP, and
other protocols to find vulnerabilities and gain further access. However, determining that a device is not
genuinely a disk station—without physically interacting with it—can be extremely challenging for them.
Selecting the right honeypot can be a challenging decision, as there are many options,
each with its own advantages. Here are some types to consider:
Pure
Honeypots:
Pure honeypots replicate full production systems. They are high maintenance but can
be very effective.
Production Honeypots:
Honeypots can be
integrated directly into production software without additional devices. For example, in web applications, you
can create certain links that should not be accessed or forms that should not be submitted.
High-Interaction Honeypots:
High-interaction honeypots replicate full
services or devices, keeping attackers engaged for longer periods and allowing you to gather more information
about the attack.
Low-Interaction Honeypots:
Low-interaction
honeypots mimic only a specific part of a service. They are easier to maintain and offer a smaller attack
surface for vulnerabilities.
For more options, the honeynet.org project provides a comprehensive list: honeynet.org.

What’s the right strategy for placement? To effectively deploy honeypots for internal
detection, strategically place them near high-value assets like data storage systems or databases and in each
network segment. Ensure they blend in with the environment by using realistic data or mimicking the physical
devices present in the network.
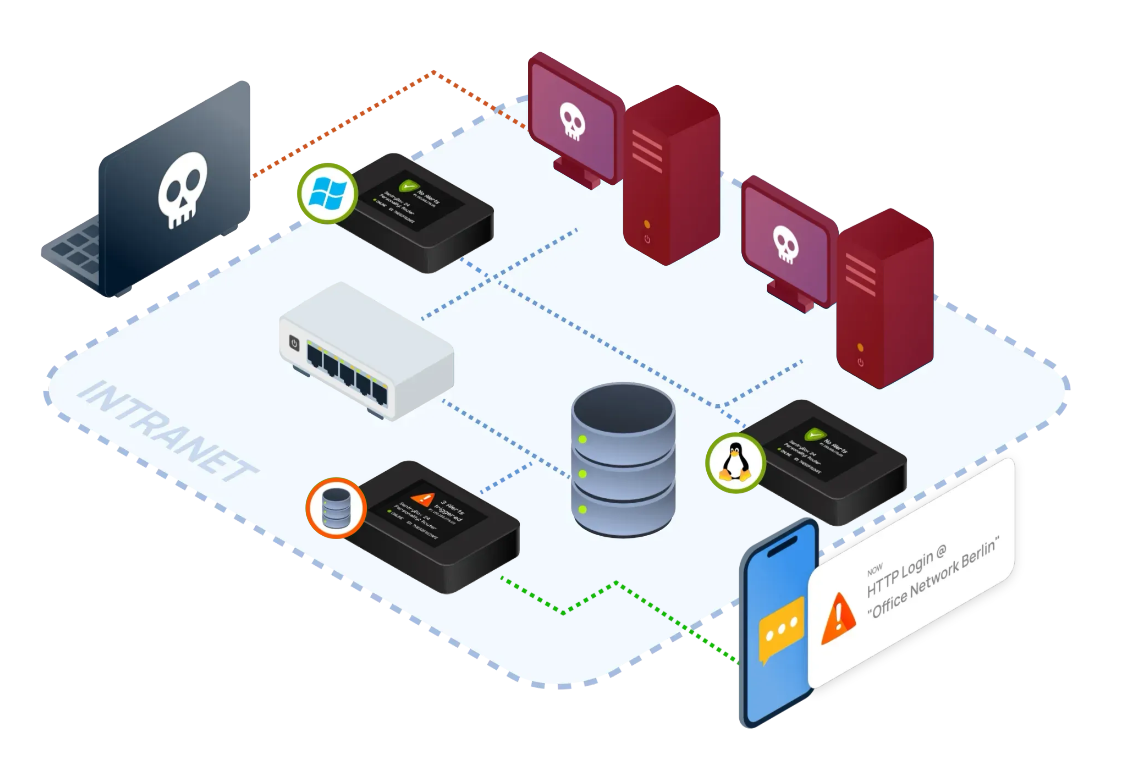
At some point, attackers will interact with the honeypot—either to identify the type of
device or to attempt hacking it. These interactions will be reported, including the credentials used and the
source device that has already been compromised.
Honeypots are strategically placed within networks to lure hackers, and that is
precisely what makes them valuable.